What is Inverter?
An inverter refers to a device that can convert direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. It is commonly used in industrial automation systems to control AC motors.
AC motors are widely used in automation applications because of their high efficiency, controllability, and ability to handle significant power requirements. However, they need AC power to operate. Since many industrial automation systems rely on DC power sources such as batteries or rectifiers, we need inverter to convert the DC power to the required AC power. The inverter takes a DC input and converts it to a variable-frequency AC output. By adjusting the frequency and voltage of the output, the speed and torque of the connected AC motor can be precisely controlled. This enables flexible and efficient motor control in automation systems. Big Diamond as an automation equipment dealer in GCC can provide you various type of invertor from well-known producer. For any inquiries, please contact us.
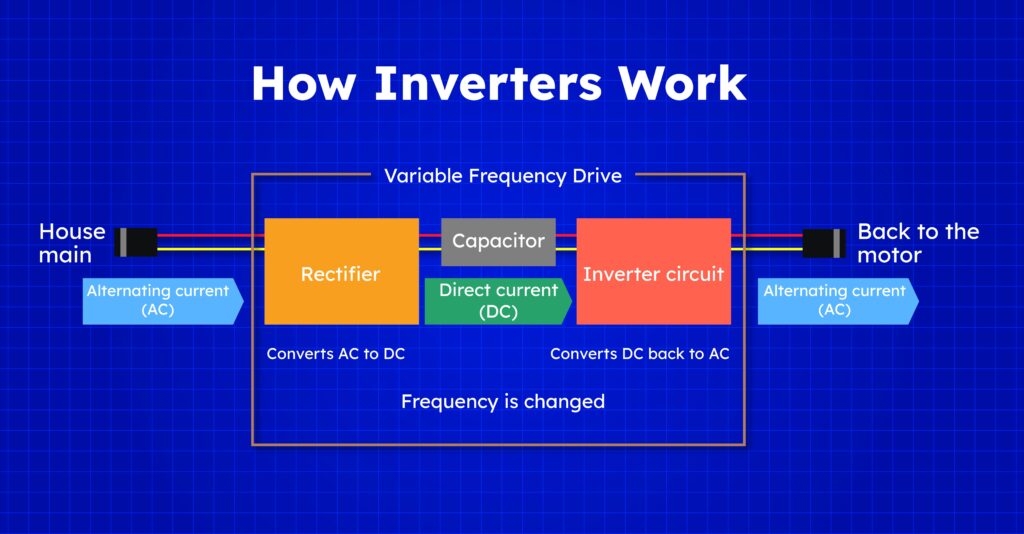
How Inverter works?
The basic inverter system consists of an integrated set of electronic components that convert DC power to AC power. Here is a brief description of how an inverter works.
1 – Rectification: The first stage of the inverter is the rectification system. It involves converting the incoming AC power to DC power. This is usually accomplished by using a rectifier, with diodes capable of conducting current in only one direction. The rectifier circuitry ensures that the DC voltage received from the AC input is relatively weak.
2 – DC Bus: The prepared DC voltage is then stored in a device called DC bus. The DC bus acts as an intermediate storage device before the DC power is converted back to AC.
3 – Inversion: The next step is inversion process. The DC voltage from the DC bus is transferred to the inverter circuit, which contains switches (usually insulated gate bipolar transistors, or IGBTs) that rapidly turn on and off if the inverter circuit obeys the switching pattern of these transistors it generates pulses of AC waveform.
4 – Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): To achieve variable AC frequency, the inverter uses a technique called Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). This modulation method allows the inverter to control the effective voltage and frequency of the AC output.
5 – Output filter: The output of the inverter consisting of a series of pulses is then passed through an output filter. The filter smooths the waveform by removing high-frequency components and produces a sinusoidal AC waveform similar to the desired output frequency voltage.
6 – AC Output: The filtered AC waveform is then sent to the load, typically an AC motor or another device that calls for AC electricity for operation. The motor or tool related to the inverter may be controlled by means of adjusting the inverter’s output frequency and voltage.
The process described above is a simple overview of how an inverter works. In practice, modern inverters may have additional components and circuitry to increase efficiency, protect against faults, and enable control and monitoring of different components.
Inverter features:
Using Inverter in automation and industrial programs often have numerous functions that enhance their overall performance, manipulate skills, and usual functionality. Here are some common features for inverter:
- Variable Frequency Control
- Voltage Control
- Acceleration and Deceleration Control
- Overload Protection
- Energy Efficiency and Power Savings
- Fault Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
- Reduce output noise
- Reducing engine damage and increasing durability
Kinds of Invertors:
Several types of inverters are available, and each is designed for specific applications and power conversion requirements. Here are some common types of inverters.
1 – Standalone/Standard Inverters: These inverters are designed to operate independently and are typically used in off-grid applications, such as remote locations or mobile setups where the utility grid cannot be connected Standalone inverters are typically powered by renewable sources (such as solar panels or wind turbines). etc.) has a battery bank that stores energy and provides AC power when needed.
2 – Grid-tied inverters: These inverters are used in grid-connected systems, where DC power from renewable sources (such as solar panels) is converted into AC power that can be fed back into the utility grid -tied inverters frequency their output grid voltage -Synchronized with, in order to export the excess power, usually have no battery storage.
3 – Hybrid Inverters: Hybrid inverters combine the performance of independent and grid-tied inverters. They can operate in both off-grid and grid-connected modes, providing flexibility and flexibility. Hybrid inverters are often used in systems that combine renewable energy, battery storage, and the ability to switch between grid and off-grid modes as needed.
4 – Central Inverters: Central inverters are typically used in large PV installations, such as solar farms or utilities. They handle high power efficiency and convert DC power from multiple grids or an array of solar panels into AC power. Central inverters are known for their efficiency and are usually installed in dedicated inverter stations.
It is important to choose the right inverter based on the specific application, power requirements and system configuration. Consulting with experts or professionals in the industry can help determine the most appropriate inverter for a given project or system.
Advantages of using Inverter In automation:
- 1. Power Conversion: The main advantage of using an inverter is its ability to convert DC power to AC power. This takes advantage of AC-powered appliances and appliances, which are increasing in popularity and widely used in many applications.
- 2. Variable Speed Control: Inverters provide precise control of AC motors and adjustable speed control. This feature is particularly useful in automation systems, as it enables better control of motor-driven processes, resulting in improved efficiency, lower energy consumption and higher system performance.
- 3. Energy efficiency: Inverters contribute to energy efficiency by adjusting the output frequency and voltage to suit the requirements of a particular load. By delivering the exact amount of energy needed, inverters reduce energy consumption, resulting in lower energy costs and a lower environmental impact.
- 4. Fault protection and diagnosis: Inverters usually have built-in safety devices and power diagnosis. These features monitor motor and system parameters, detect faults or abnormalities, and provide early warning signals. By detecting problems early, inverters help prevent motor damage, reduce downtime, and facilitate efficient troubleshooting.
- 5. Flexibility and adaptability: Inverters are versatile devices that can be customized to meet specific application requirements. It can be integrated into a wide range of systems and networks, allowing for configuration flexibility to adapt to changing business requirements.
Inverter usage:
Inverters have a wide range of applications in different industries. Some common inverter uses are mentioned below:
1 – Industrial Automation: Inverters are widely used to control AC motors in industrial automation systems, enabling variable speed control and precise control of mechanically driven processes They find advantages in manufacturing, wiring assemblers, conveyors, pumps, fans, and other industrial equipment. Inverter in automation is one most important part in system.
2 – Renewable energy systems: Inverters play an important role in converting DC power from renewable sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, into usable AC power They provide power clean alongside power grids, powering homes, businesses and communities.
3 – Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers: Inverters are used in EV charging infrastructure to convert AC power from the grid to DC power to charge electric vehicle batteries They ensure proper and controlled charging, and power to roads two so for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) as well ) applications.
4 – Disaster and emergency relief: Inverters are essential in emergency response and disaster situations, they can be used to power medical facilities, temporary shelters, communication systems and emergency equipment providing temporary power in areas where affected by natural disasters or other emergencies.
These are just a few examples of inverters. Their versatility and ability to convert DC power to AC power make them indispensable in many applications, resulting in improved performance, energy savings and energy reliability. Big Diamond as an automation equipment supplier in Oman and GCC countries can supply variety of inverters in automation from well-known producer in these countries. You can order all kind of automation equipment for your factories such as invertors, gearboxes, servo motor and drives, VFD, HMI, etc. from Big Diamond Company. For any inquiries, please contact us.

